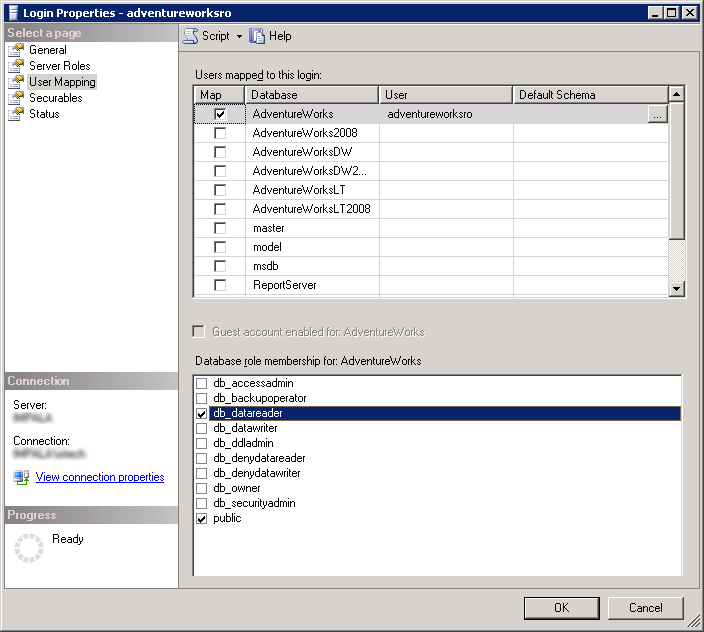
Using SQL Server Management Studio 2008:
- Connect to your database server.
- Expand Security > Logins.
- Right-click on the user who will be set as having read-only access (in this example "adventureworksro").
- Select Properties.
- Select User Mapping.
- Map the login to the database they will have access to.
- Tick the boxes for role membership next to public and db_datareader.
- Confirm by clicking OK.
Database-level role names
from http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms189121(SQL.100).aspxdb_accessadmin
Members of the db_accessadmin fixed database role can add or remove access to the database for Windows logins, Windows groups, and SQL Server logins.
db_backupoperator
Members of the db_backupoperator fixed database role can back up the database.
db_datareader
Members of the db_datareader fixed database role can read all data from all user tables.
db_datawriter
Members of the db_datawriter fixed database role can add, delete, or change data in all user tables.
db_ddladmin
Members of the db_ddladmin fixed database role can run any Data Definition Language (DDL) command in a database.
db_denydatareader
Members of the db_denydatareader fixed database role cannot read any data in the user tables within a database.
db_denydatawriter
Members of the db_denydatawriter fixed database role cannot add, modify, or delete any data in the user tables within a database.
db_owner
Members of the db_owner fixed database role can perform all configuration and maintenance activities on the database, and can also drop the database.
db_securityadmin
Members of the db_securityadmin fixed database role can modify role membership and manage permissions. Adding principals to this role could enable unintended privilege escalation.
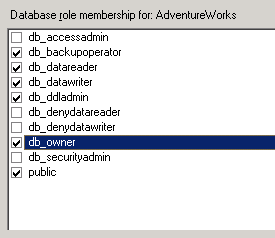
In theory, a user who can do nearly everything but modify access and security permissions:
Category: Databases :: Article: 306



 Like
Like  wow it works grat
wow it works grat










I'm so jealous as we're still on SQL Server 2008 R2. I'm also not 100% sure if the problem happens in v2012 for security reasons. I figure you add users to individual databases and not to the overall database server. The creating user will more than often have db_owner privileges. I can only suggest checking the other databases that this user is not allowed to access and set the db_denydatareader for them...